Azure Active Directory: 7 Powerful Insights You Must Know
Ever wondered how millions of businesses securely manage user access across cloud apps? The answer often lies in Azure Active Directory—a game-changer in identity and access management. Let’s dive into what makes it so powerful.
What Is Azure Active Directory?

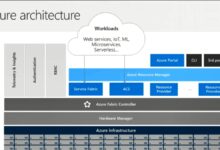
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service, designed to help organizations securely manage user identities and control access to applications and resources. Unlike traditional on-premises Active Directory, Azure AD is built for the cloud, supporting modern authentication protocols and hybrid environments.
Core Purpose of Azure AD
The primary goal of Azure Active Directory is to provide single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and centralized identity governance across cloud and on-premises applications. It enables users to log in once and gain access to multiple systems without re-entering credentials.
- Enables secure access to SaaS apps like Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
- Supports identity federation with on-premises directories via Azure AD Connect.
- Facilitates conditional access policies based on user location, device health, and risk level.
Differences Between Azure AD and On-Premises AD
While both systems manage identities, they serve different architectures. On-premises Active Directory is based on Windows Server and uses LDAP, Kerberos, and NTLM protocols. In contrast, Azure AD is a REST-based, HTTP/HTTPS-driven service optimized for cloud scalability.
- Azure AD does not use domain controllers or Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in the traditional sense.
- It’s not a direct replacement but rather a complement to on-premises AD, especially in hybrid setups.
- Object synchronization is handled via Azure AD Connect, which syncs users, groups, and passwords from on-prem to the cloud.
“Azure Active Directory is not just ‘Active Directory in the cloud’—it’s a fundamentally different platform designed for modern identity needs.” — Microsoft Documentation
Key Features of Azure Active Directory
Azure AD offers a robust suite of features that empower organizations to manage digital identities efficiently. These capabilities are essential for securing access in today’s distributed work environments.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single sign-on allows users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without logging in repeatedly. Azure AD supports SSO for thousands of pre-integrated SaaS apps and custom enterprise applications.
- Users can access apps via the My Apps portal or Microsoft 365 dashboard.
- SSO methods include password-based, SAML, OpenID Connect, and OAuth 2.0.
- Administrators can configure app-specific settings like sign-on URLs and reply URLs.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Security is paramount, and Azure AD’s MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity using two or more methods—something they know (password), something they have (phone or token), or something they are (biometrics).
azure active directory – Azure active directory menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- MFA can be enforced globally or conditionally based on risk, location, or device compliance.
- Available verification methods include phone calls, text messages, Microsoft Authenticator app, FIDO2 security keys, and biometric prompts.
- According to Microsoft, MFA blocks over 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
Conditional Access
Conditional Access is one of the most powerful tools in Azure AD. It allows administrators to define policies that grant or deny access based on specific conditions such as user role, IP address, device state, or sign-in risk.
- Policies can require MFA, compliant devices, or approved client apps before granting access.
- Integration with Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps enhances visibility into risky sign-ins.
- Example: Block access from unfamiliar locations unless the user passes MFA and uses a managed device.
Azure AD Editions: Free, P1, and P2 Compared
Azure Active Directory comes in four main editions: Free, Office 365 apps (included with M365), Premium P1, and Premium P2. Each tier unlocks progressively advanced features tailored to organizational needs.
Azure AD Free Edition
The Free edition is included with any Azure subscription and provides basic identity and access management capabilities.
- Supports up to 50,000 directory objects (users, groups, contacts).
- Includes SSO, self-service password reset for cloud users, and basic group management.
- Limited reporting and no conditional access policies.
Azure AD Premium P1
Premium P1 builds on the Free edition with advanced access control and identity management features.
- Enables conditional access, dynamic groups, and self-service application access.
- Supports hybrid identity with writeback capabilities (e.g., password writeback, device writeback).
- Includes Azure AD Identity Protection for detecting risky sign-ins and user risks.
Azure AD Premium P2
Premium P2 adds identity governance and advanced security analytics, making it ideal for compliance-heavy industries.
- Includes Identity Governance features like access reviews, entitlement management, and privileged identity management (PIM).
- Provides full-featured Identity Protection with risk-based policies and automated remediation.
- Enables long-term risk and sign-in trend analysis for proactive threat detection.
“Choosing the right Azure AD edition depends on your organization’s size, security requirements, and compliance goals.” — Microsoft Azure Pricing Guide
Hybrid Identity with Azure Active Directory
For organizations transitioning from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, hybrid identity is a critical strategy. Azure AD enables seamless integration between on-prem Active Directory and cloud services, ensuring users have consistent access across environments.
What Is Hybrid Identity?
Hybrid identity refers to the synchronization of user identities from an on-premises directory (like Windows Server AD) to Azure AD. This allows users to use the same credentials for both local and cloud resources, improving user experience and simplifying management.
azure active directory – Azure active directory menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Users authenticate against Azure AD when accessing cloud apps.
- Password hash synchronization or pass-through authentication ensures secure credential validation.
- Seamless SSO can be enabled for domain-joined devices accessing cloud apps.
Azure AD Connect: The Bridge to the Cloud
Azure AD Connect is the primary tool used to establish and maintain hybrid identity. It replaces older tools like DirSync and Azure AD Sync.
- Automatically synchronizes user accounts, groups, contacts, and passwords from on-prem AD to Azure AD.
- Supports filtering to sync only specific OUs or domains.
- Can be configured for high availability with staging servers.
Authentication Methods in Hybrid Environments
Organizations can choose from several authentication methods when implementing hybrid identity:
- Password Hash Synchronization (PHS): Syncs hashed passwords from on-prem AD to Azure AD. Simple to set up and widely used.
- Pass-Through Authentication (PTA): Validates user credentials against on-prem AD in real time without storing passwords in the cloud. Offers faster sign-in and better security.
- Federation (AD FS): Uses on-premises federation servers (like AD FS) to authenticate users. Provides full control over authentication but requires more infrastructure.
Identity Governance and Access Management
As organizations grow, managing who has access to what becomes increasingly complex. Azure Active Directory provides comprehensive identity governance tools to ensure least-privilege access and regulatory compliance.
Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a feature available in Azure AD Premium P2 that helps organizations manage, control, and monitor access to critical resources.
- Enables just-in-time (JIT) access, where admins request elevated privileges only when needed.
- Requires approval workflows and multi-factor authentication for privilege activation.
- Provides audit logs and time-bound role assignments to reduce standing access.
Access Reviews
Access reviews allow administrators to periodically review and confirm whether users should retain access to apps, groups, or roles.
- Automated reviews can be scheduled monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Reviewers can be managers, group owners, or designated compliance officers.
- Unused or unnecessary access can be automatically removed after review.
Entitlement Management
Entitlement management enables organizations to create access packages—collections of resources that users can request access to based on business policies.
- Supports approval workflows, access expiration, and certification.
- Integrates with external users (B2B) for partner or contractor access.
- Reduces administrative overhead by automating access lifecycle management.
“Identity governance isn’t just about security—it’s about accountability, compliance, and operational efficiency.” — Gartner Research
Security and Threat Protection in Azure AD
In an era of rising cyber threats, Azure Active Directory plays a crucial role in protecting organizational identities. Its built-in security tools help detect, respond to, and prevent identity-based attacks.
azure active directory – Azure active directory menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Azure AD Identity Protection
Identity Protection uses machine learning and risk detection to identify suspicious activities such as sign-ins from anonymous IPs, unfamiliar locations, or impossible travel.
- Assigns risk levels (low, medium, high) to users and sign-ins.
- Triggers automated responses like requiring MFA or blocking access.
- Integrates with Conditional Access to enforce risk-based policies.
Sign-In Logs and Audit Logs
Detailed logging is essential for monitoring and forensic analysis. Azure AD provides two main types of logs:
- Sign-in logs: Capture details about user authentication attempts, including success/failure, IP address, device, and application accessed.
- Audit logs: Record administrative activities like user creation, role assignment changes, and policy modifications.
- Logs can be exported to Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, or SIEM tools like Splunk for advanced analysis.
Identity Secure Score
The Identity Secure Score is a metric provided by Microsoft that evaluates an organization’s security posture in Azure AD.
- Measures how well security best practices are implemented (e.g., MFA enrollment, risk policy configuration).
- Provides actionable recommendations to improve security.
- Available in the Azure portal under Azure AD > Security > Secure Score.
Azure AD B2C and B2B: Extending Identity Beyond Employees
While Azure AD is primarily designed for internal users (employees), Microsoft also offers specialized services for external identity scenarios: Azure AD B2C and Azure AD B2B.
Azure AD B2C: Customer Identity Management
Azure AD B2C (Business-to-Consumer) is a customer identity and access management (CIAM) solution that allows organizations to manage millions of external user identities.
- Used for consumer-facing apps like e-commerce, mobile banking, or health portals.
- Supports social identity providers (Google, Facebook, Apple) and local account sign-up.
- Highly customizable with branding, user flows, and API connectors.
Azure AD B2B: Collaborating with Partners
Azure AD B2B (Business-to-Business) enables secure collaboration with external users from partner organizations.
- Guest users can be invited via email and authenticate using their own organizational credentials.
- Access can be granted to specific apps, SharePoint sites, or Teams channels.
- Administrators retain control over permissions and can revoke access at any time.
Key Differences Between B2C, B2B, and Core Azure AD
Understanding the distinctions between these services is crucial for proper implementation:
azure active directory – Azure active directory menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Core Azure AD: For managing internal employees and resources.
- Azure AD B2B: For inviting external partners with limited access to corporate resources.
- Azure AD B2C: For managing large-scale consumer identities with self-service capabilities.
“Choosing the right Azure AD service depends on whether your users are employees, partners, or customers.” — Microsoft Azure Architecture Center
Best Practices for Managing Azure Active Directory
Implementing Azure AD is just the beginning. To maximize security, performance, and user experience, organizations should follow proven best practices.
Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA is the single most effective way to prevent unauthorized access. Organizations should require MFA for all users, especially administrators.
- Use phishing-resistant methods like FIDO2 security keys or the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Enable MFA registration during user onboarding.
- Monitor MFA registration rates via the Azure AD portal.
Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC ensures users have only the permissions they need to perform their jobs. Avoid assigning global administrator roles unnecessarily.
- Create custom roles with minimal required permissions.
- Use PIM for just-in-time elevation of privileges.
- Regularly review role assignments and remove unused access.
Monitor and Respond to Security Alerts
Proactive monitoring helps detect threats before they escalate. Use Azure AD’s built-in tools to stay ahead of risks.
- Set up alerts for high-risk sign-ins or unusual activity.
- Integrate with Microsoft Sentinel for advanced threat hunting.
- Conduct regular security assessments using the Identity Secure Score.
What is Azure Active Directory used for?
Azure Active Directory is used to manage user identities and control access to cloud and on-premises applications. It enables single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, conditional access, and identity governance for organizations of all sizes.
Is Azure AD the same as Windows Active Directory?
azure active directory – Azure active directory menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
No, Azure AD is not the same as Windows Active Directory. While both manage identities, Azure AD is cloud-native and designed for modern authentication protocols, whereas Windows AD is on-premises and relies on legacy protocols like LDAP and Kerberos.
How much does Azure Active Directory cost?
Azure AD has a Free tier included with Azure subscriptions. Premium P1 costs around $6/user/month, and Premium P2 is about $9/user/month. Pricing varies based on licensing and volume discounts.
Can Azure AD replace on-premises Active Directory?
Azure AD can complement but not fully replace on-premises Active Directory in most cases. Organizations with legacy applications or Group Policy dependencies still need on-prem AD. However, Microsoft is moving toward cloud-only models with Azure AD DS and Windows 365.
What is the difference between Azure AD and Microsoft Entra ID?
As of 2023, Microsoft has rebranded Azure Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID. The service remains the same, but the new name reflects its role as part of the broader Microsoft Entra suite of identity products.
azure active directory – Azure active directory menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
In conclusion, Azure Active Directory is a cornerstone of modern identity management. Whether you’re securing employee access, enabling hybrid work, or managing customer identities at scale, Azure AD provides the tools you need. From robust security features like MFA and conditional access to advanced governance with PIM and access reviews, it empowers organizations to stay secure and compliant in a cloud-first world. By understanding its capabilities, editions, and best practices, businesses can unlock the full potential of identity-driven security.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: