Azure Login Portal: 7 Ultimate Tips for Seamless Access
Accessing the Azure login portal doesn’t have to be complicated. Whether you’re a cloud beginner or an experienced admin, mastering this gateway is essential for managing your Microsoft cloud services efficiently and securely.
Understanding the Azure Login Portal

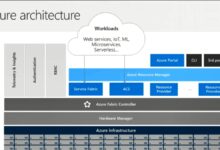
The Azure login portal is the primary entry point for users to access Microsoft Azure’s vast ecosystem of cloud computing services. It serves as a centralized dashboard where administrators, developers, and business users can manage virtual machines, storage, networking, security, and more—all through a web-based interface. The portal is accessible at portal.azure.com, and it integrates tightly with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) for identity and access management.
What Is the Azure Login Portal?
The Azure login portal is more than just a login screen—it’s a comprehensive management console. Once authenticated, users are directed to the Azure portal interface, where they can deploy, monitor, and manage resources across global data centers. It supports role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and seamless integration with other Microsoft 365 services.
- Centralized access to cloud resources
- Integrated with Microsoft Entra ID for secure authentication
- Available globally with regional data center support
How It Differs From Other Microsoft Logins
While Microsoft accounts (like Outlook.com) allow personal access to consumer services, the Azure login portal is designed for enterprise and developer use. It relies on organizational identities managed through Microsoft Entra ID, not personal Microsoft accounts (unless explicitly invited as guests). This distinction ensures that business data remains secure and governed under corporate policies.
“The Azure portal is the nerve center of your cloud operations—secure access isn’t optional, it’s foundational.” — Microsoft Cloud Architecture Team
Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing the Azure Login Portal
Logging into the Azure portal is straightforward, but understanding each step ensures you avoid common pitfalls. Whether you’re accessing Azure for the first time or troubleshooting login issues, following a structured approach helps maintain security and efficiency.
Navigating to the Correct URL
Always start by visiting the official Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com. Avoid third-party links or search engine results that may lead to phishing sites. Bookmarking the correct URL is a best practice for security-conscious users.
- Use HTTPS to ensure encrypted communication
- Verify the domain name to prevent phishing attacks
- Consider using Microsoft’s official app for mobile access
Entering Credentials Correctly
After reaching the login page, enter your work or school email address associated with your Azure subscription. This is typically in the format username@yourcompany.com, not a personal @outlook.com or @hotmail.com account (unless configured otherwise). After entering the email, the system will prompt for a password and, if enabled, multi-factor authentication.
- Ensure Caps Lock is off when typing passwords
- Use a password manager to avoid typos
- Check your keyboard layout if using non-English characters
Authentication Methods Supported by the Azure Login Portal
The Azure login portal supports multiple authentication methods to balance security and usability. Organizations can configure these based on compliance requirements, user roles, and risk tolerance.
Password-Based Authentication
This is the most basic method, where users enter a username and password. While simple, it’s also the most vulnerable to attacks like brute force or credential stuffing. Microsoft recommends enforcing strong password policies and combining this with additional security layers.
- Minimum 8-character length with complexity rules
- Password expiration policies (though Microsoft now advises against frequent resets)
- Integration with Azure AD Password Protection to block weak passwords
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds a critical second layer of security. After entering a password, users must verify their identity using a second factor—such as a phone call, text message, authenticator app, or biometric confirmation. Microsoft strongly recommends enabling MFA for all users, especially administrators.
- Microsoft Authenticator app supports push notifications and time-based codes
- Hardware tokens (FIDO2) offer phishing-resistant authentication
- Conditional Access policies can enforce MFA based on risk level or location
According to Microsoft, accounts with MFA enabled are over 99.9% less likely to be compromised.
Common Issues When Using the Azure Login Portal
Even experienced users encounter issues when logging into the Azure portal. Recognizing common problems and their solutions can save time and reduce frustration.
Forgot Password or Locked Account
Users often forget their passwords or get locked out after multiple failed attempts. The Azure login portal provides a ‘Forgot password?’ link that guides users through a self-service password reset (SSPR) process, provided it’s been configured by the administrator.
- SSPR requires pre-registered contact methods (email, phone, or authenticator app)
- Administrators can unlock accounts manually via the Microsoft 365 admin center
- Lockout duration is typically 30 minutes by default
Location or Browser Compatibility Issues
Sometimes, users cannot log in due to browser incompatibility or geographic restrictions. The Azure portal works best on modern browsers like Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Safari. Additionally, some organizations use Conditional Access policies that block logins from certain countries or IP ranges.
- Clear browser cache and cookies before retrying
- Disable browser extensions that may interfere with scripts
- Try incognito/private mode to rule out extension conflicts
Security Best Practices for the Azure Login Portal
Securing access to the Azure login portal is paramount. A compromised account can lead to data breaches, unauthorized resource deployment, or even ransomware attacks. Implementing robust security practices protects both your organization and its cloud assets.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication for All Users
As previously mentioned, MFA is one of the most effective defenses against unauthorized access. Administrators should enforce MFA for all users, especially those with elevated privileges. This can be done through the Microsoft Entra admin center under ‘Security’ > ‘Multi-factor authentication’.
- Use the ‘Conditional Access’ feature to require MFA for sensitive operations
- Register multiple verification methods per user for redundancy
- Monitor sign-in logs for suspicious activity
Using Conditional Access Policies
Conditional Access (CA) allows organizations to define rules that control how and when users can access the Azure portal. For example, you can block logins from untrusted locations, require compliant devices, or enforce MFA during high-risk sign-ins.
- Create policies based on user risk, device compliance, or location
- Test policies in ‘Report-only’ mode before enforcement
- Use CA to block legacy authentication protocols (e.g., IMAP, SMTP)
“Conditional Access is the cornerstone of Zero Trust security in Azure.” — Microsoft Security Documentation
Managing Multiple Subscriptions via the Azure Login Portal
Many organizations and individuals manage multiple Azure subscriptions—whether for different departments, projects, or environments (development, testing, production). The Azure login portal provides tools to switch between subscriptions seamlessly and manage them efficiently.
Switching Between Subscriptions
Once logged in, users can switch between subscriptions they have access to by clicking their profile icon in the top-right corner and selecting ‘Switch directory’ or ‘Change directory’. Alternatively, the subscription filter in the portal’s main menu allows quick navigation across resources.
- Use the ‘Directory + Subscription’ filter to manage cross-tenant access
- Pin frequently used subscriptions for faster access
- Ensure proper RBAC roles are assigned per subscription
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) Explained
RBAC is a key feature of the Azure login portal that allows fine-grained control over who can do what within a subscription. Roles like ‘Owner’, ‘Contributor’, and ‘Reader’ define permissions, and custom roles can be created for specific needs.
- Assign roles at the subscription, resource group, or individual resource level
- Follow the principle of least privilege (PoLP)
- Regularly audit role assignments using Azure Advisor
Advanced Features of the Azure Login Portal
Beyond basic login and navigation, the Azure portal offers advanced tools that enhance productivity, automation, and monitoring. These features are essential for DevOps teams, cloud architects, and security professionals.
Using Azure Cloud Shell
Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based command-line interface accessible directly from the portal. It supports both Bash and PowerShell environments and comes pre-configured with CLI tools like Azure CLI, Terraform, and kubectl.
- No installation required—runs in the browser
- Persistent storage via Azure File Shares
- Perfect for scripting, automation, and troubleshooting
Custom Dashboards and Monitoring Tools
Users can create personalized dashboards to monitor key metrics, resource health, and cost trends. These dashboards can include charts, logs, and alerts from services like Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, and Application Insights.
- Share dashboards across teams for collaborative monitoring
- Set up alerts for CPU usage, storage limits, or budget thresholds
- Integrate with Power BI for advanced reporting
“A well-designed dashboard can reduce incident response time by up to 40%.” — Azure Operations Guide
Troubleshooting and Support for the Azure Login Portal
Even with best practices in place, issues can arise. Knowing where to find help and how to diagnose problems is crucial for maintaining uptime and productivity.
Using Azure Advisor for Guidance
Azure Advisor is a built-in tool that provides personalized recommendations for improving performance, security, cost, and reliability. It can detect misconfigurations related to authentication, RBAC, and MFA settings.
- Review security recommendations regularly
- Follow cost optimization tips to avoid billing surprises
- Enable Advisor alerts for critical findings
Contacting Microsoft Support
For persistent login issues or service outages, contacting Microsoft Support is the next step. Support plans range from basic (free) to premier (paid), offering varying response times and technical depth.
- Open a support ticket directly from the Azure portal
- Provide detailed logs and screenshots for faster resolution
- Use the Azure Status page to check for ongoing outages
How do I log in to the Azure portal?
To log in to the Azure portal, go to portal.azure.com, enter your work or school email address, and input your password. If multi-factor authentication is enabled, complete the second verification step using your preferred method (app, phone, or token).
What should I do if I can’t access the Azure login portal?
If you can’t access the Azure login portal, first check your internet connection and try a different browser. Ensure you’re using the correct URL and credentials. If MFA is required, verify your secondary method is working. If issues persist, use the ‘Forgot password?’ option or contact your administrator.
Is the Azure login portal secure?
Yes, the Azure login portal is highly secure when best practices are followed. Enabling multi-factor authentication, using Conditional Access policies, and applying role-based access control significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Microsoft continuously monitors and updates the platform for security threats.
Can I manage multiple Azure accounts from one login?
Yes, you can manage multiple Azure subscriptions and directories from a single login. Use the ‘Directory + Subscription’ filter in the portal to switch between environments. Ensure you have the appropriate permissions assigned in each subscription.
How do I enable MFA for my Azure account?
MFA can be enabled by an administrator through the Microsoft Entra admin center. Navigate to ‘Users’ > ‘Multi-factor authentication’ and enable it for the desired users. Alternatively, users can set it up via their account settings if self-service is allowed.
Mastering the Azure login portal is essential for anyone working with Microsoft’s cloud platform. From secure authentication and role-based access to advanced monitoring and troubleshooting, the portal offers a powerful suite of tools. By following best practices—like enabling MFA, using Conditional Access, and leveraging Azure Advisor—you can ensure secure, efficient, and reliable access to your cloud resources. Whether you’re a developer, administrator, or business user, understanding the full capabilities of the Azure login portal empowers you to make the most of the cloud.
Further Reading: