Azure Portal: 7 Powerful Features You Must Master Today
Welcome to the ultimate guide on the Azure Portal — your command center for managing Microsoft’s cloud empire. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, mastering this platform unlocks efficiency, control, and innovation like never before.
What Is the Azure Portal?

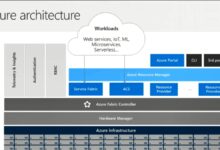
The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services, resources, and subscriptions across the Azure ecosystem. It provides a centralized dashboard where users can deploy, monitor, and manage virtual machines, storage accounts, databases, networking tools, and more — all through an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI).
Core Purpose and Functionality
The primary goal of the Azure Portal is to simplify cloud management. Instead of relying solely on command-line tools or scripts, users can visually interact with their cloud infrastructure. This makes it ideal for teams that include non-developers, such as IT administrators, project managers, and business analysts.
- Provides real-time monitoring of resource performance
- Enables drag-and-drop deployment of preconfigured templates
- Supports role-based access control (RBAC) for secure collaboration
How It Compares to Other Management Tools
While tools like Azure CLI, PowerShell, and Azure DevOps offer powerful automation capabilities, the Azure Portal stands out for its accessibility. It doesn’t require deep coding knowledge, making it perfect for quick troubleshooting, visual diagnostics, and initial setup tasks.
“The Azure Portal is the gateway to Azure — simple enough for beginners, yet robust enough for enterprise-scale operations.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Key Features of the Azure Portal
The Azure Portal isn’t just a dashboard; it’s a feature-rich environment designed to streamline every aspect of cloud management. From resource creation to cost tracking, here are the standout capabilities that make it indispensable.
Resource Groups and Management
One of the foundational concepts in the Azure Portal is the use of resource groups. These are logical containers that group related resources for easier management, billing, and lifecycle control.
- You can apply policies and permissions at the resource group level
- Deleting a resource group removes all associated resources, simplifying cleanup
- Great for organizing environments like dev, staging, and production
Marketplace and Template Deployment
The Azure Marketplace within the portal offers thousands of pre-built solutions from Microsoft and third-party vendors. Whether you need a WordPress site, a machine learning model, or a firewall appliance, you can deploy it with just a few clicks.
- Templates follow Infrastructure as Code (IaC) principles using ARM (Azure Resource Manager) templates
- Custom templates can be saved and reused across teams
- Integration with GitHub allows version-controlled deployments
Monitoring and Diagnostics with Azure Monitor
Azure Monitor is deeply integrated into the portal, giving you real-time insights into application performance, server health, and network traffic. You can set up alerts, view logs, and create custom dashboards tailored to your needs.
- Collect metrics from VMs, apps, and containers
- Set up alert rules based on thresholds (e.g., CPU usage over 80%)
- Visualize data using charts and time-series graphs
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface
Understanding the layout of the Azure Portal is crucial for efficient navigation. Once you log in, you’re greeted with a customizable dashboard filled with widgets, shortcuts, and live data feeds.
Dashboard and Customization Options
The default dashboard can be personalized to display only the information relevant to your role. For example, a database administrator might pin SQL database performance tiles, while a network engineer focuses on virtual network status.
- Drag and drop tiles to rearrange your view
- Save multiple dashboards for different projects or roles
- Share dashboards with team members for collaborative oversight
Search and Quick Access Bar
At the top of the portal is a powerful search bar that lets you find any service, resource, or setting instantly. Typing “VM” brings up Virtual Machines, related documentation, and common actions.
- Search results include both services and support articles
- Recent resources are auto-suggested for faster access
- Can filter results by resource type, region, or subscription
Navigation Menu and Hub Structure
The left-hand navigation menu acts as the central hub for all Azure services. It’s organized into categories like ‘All services’, ‘Favorites’, and ‘Recent resources’. You can also pin frequently used services for one-click access.
- Favorites let you streamline access to critical tools like Storage Accounts or App Services
- Service categories are grouped by function (Compute, Networking, Security, etc.)
- Dynamic updates reflect new services added by Microsoft
Managing Azure Resources via the Portal
One of the most powerful aspects of the Azure Portal is its ability to manage resources seamlessly. Whether you’re provisioning a new virtual machine or scaling a web app, the portal guides you through each step with wizards and validation checks.
Creating and Configuring Virtual Machines
Deploying a virtual machine (VM) in the Azure Portal is straightforward. You select the OS, size, region, and authentication method through a guided form. Advanced options allow you to attach disks, configure networking, and enable monitoring.
- Choose between Windows and Linux distributions
- Select VM sizes based on vCPUs, memory, and GPU needs
- Enable auto-shutdown to reduce costs during idle hours
Setting Up Storage Accounts and Blob Services
Storage accounts are essential for storing unstructured data like images, backups, and logs. Through the Azure Portal, you can create storage accounts with specific redundancy options (LRS, ZRS, GRS) and access tiers (Hot, Cool, Archive).
- Manage containers and upload blobs directly from the browser
- Set up shared access signatures (SAS) for secure file sharing
- Integrate with Azure File Sync for hybrid cloud storage
Deploying Web Apps and APIs
The Azure App Service allows you to host web applications, REST APIs, and mobile backends without managing underlying infrastructure. The portal provides deployment slots, custom domains, SSL certificates, and CI/CD integration.
- Deploy code directly from local Git, GitHub, or Azure DevOps
- Use deployment slots to test changes before going live
- Scale apps manually or automatically based on traffic
Security and Identity Management in the Azure Portal
Security is paramount in cloud environments, and the Azure Portal integrates tightly with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and other security tools to protect your resources.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC allows you to assign granular permissions to users, groups, and service principals. Instead of giving full admin rights, you can grant specific roles like ‘Reader’, ‘Contributor’, or custom roles.
- Assign roles at the subscription, resource group, or individual resource level
- Review access with the ‘Access control (IAM)’ blade
- Integrate with Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for just-in-time access
Multi-Factor Authentication and Conditional Access
To prevent unauthorized access, the Azure Portal supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies. These ensure that even if credentials are compromised, attackers can’t easily gain entry.
- Require MFA for sensitive operations or high-risk sign-ins
- Block access from untrusted locations or devices
- Enforce device compliance via Intune integration
Security Center and Compliance Monitoring
Azure Security Center (now part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud) provides unified security management and advanced threat protection. It continuously assesses your environment and recommends improvements.
- Get security recommendations like enabling disk encryption
- Detect threats using AI-driven analytics
- Ensure compliance with standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR
Cost Management and Billing Insights
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is controlling costs. The Azure Portal includes comprehensive tools to track spending, forecast budgets, and optimize resource usage.
Budgets and Cost Alerts
You can set monthly budgets and receive email alerts when spending reaches certain thresholds (e.g., 80% of budget). This helps prevent bill shock and encourages accountability across teams.
- Create budgets at the subscription or resource group level
- Filter by service, region, or tag to analyze specific costs
- Receive alerts via email or integrate with Azure Logic Apps
Cost Analysis and Optimization Reports
The Cost Analysis tool provides detailed breakdowns of your spending over time. You can visualize trends, compare months, and identify underutilized resources.
- Identify idle virtual machines that can be deallocated
- Recommend reserved instances for long-term savings
- Use the Advisor to get personalized cost-saving tips
Understanding the Pricing Calculator and Total Cost of Ownership
Before deploying resources, use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate costs. It factors in compute, storage, bandwidth, and additional services to give a realistic TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
- Compare pay-as-you-go vs. reserved instance pricing
- Factor in data transfer and egress fees
- Download estimates for stakeholder presentations
Automation and Integration Capabilities
While the Azure Portal is GUI-focused, it also supports automation and integration with external tools, bridging the gap between visual management and DevOps practices.
Using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Templates
ARM templates are JSON files that define the infrastructure and configuration of your Azure resources. They allow you to deploy entire environments consistently and repeatably.
- Export templates from existing resources in the portal
- Validate templates before deployment to catch errors
- Store templates in source control for auditability
Integration with Azure DevOps and GitHub
The Azure Portal integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines. You can trigger deployments from GitHub repositories or Azure DevOps, ensuring that code changes automatically update your cloud environment.
- Set up continuous deployment for web apps and functions
- Use YAML pipelines to automate testing and staging
- Monitor deployment history directly in the portal
PowerShell and CLI Access from the Portal
For advanced users, the Azure Portal includes a built-in Cloud Shell that provides access to Azure CLI and PowerShell. This allows you to run commands without installing anything locally.
- Access Cloud Shell directly from the top navigation bar
- Persistent storage via Azure File Share keeps your scripts safe
- Run hybrid workflows combining GUI actions with scripting
Troubleshooting and Support in the Azure Portal
Even the best-managed environments encounter issues. The Azure Portal provides tools to diagnose problems, access logs, and request support when needed.
Activity Logs and Diagnostics
Every action performed in the Azure Portal is recorded in the Activity Log. This includes who made a change, what was changed, and when it happened — crucial for auditing and incident response.
- Filter logs by resource, operation type, or time range
- Stream logs to Event Hubs or export to storage for long-term retention
- Correlate events across multiple services during outages
Using Azure Advisor for Recommendations
Azure Advisor is a personalized guide within the portal that analyzes your usage patterns and offers recommendations for performance, security, reliability, and cost.
- Get actionable tips like resizing underutilized VMs
- Improve fault tolerance by enabling availability zones
- Follow best practices for backup and disaster recovery
Accessing Support Tickets and Documentation
If you need help, the Azure Portal lets you create support tickets directly. Depending on your subscription, you can get 24/7 technical assistance, billing help, or architectural guidance.
- Submit tickets without leaving the portal
- Access official documentation and community forums
- Chat with support agents in real-time for urgent issues
Best Practices for Using the Azure Portal
To get the most out of the Azure Portal, follow these proven best practices that enhance security, efficiency, and scalability.
Organize with Tags and Naming Conventions
Use tags to categorize resources by department, environment, owner, or cost center. Combine this with consistent naming conventions (e.g., prod-web-vm-01) to make management easier.
- Apply tags during resource creation to avoid retroactive work
- Use automation to enforce tagging policies
- Generate cost reports filtered by tags
Leverage Favorites and Saved Views
Pin your most-used services to the favorites menu. Save custom dashboard views for different scenarios, such as incident response or monthly cost review.
- Reduce navigation time by up to 50%
- Create role-specific dashboards for team members
- Use saved filters in logs and cost analysis
Regularly Review Access and Permissions
Conduct periodic access reviews to ensure that only authorized users have access to critical resources. Remove stale accounts and rotate credentials regularly.
- Schedule quarterly IAM audits
- Use Azure AD Access Reviews to automate approval workflows
- Monitor for anomalous sign-in activity
What is the Azure Portal used for?
The Azure Portal is used to manage cloud resources on Microsoft Azure. It allows users to deploy, configure, monitor, and secure services like virtual machines, storage, databases, and networks through a web-based interface.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, access to the Azure Portal itself is free. However, the resources you create and manage within it (like VMs or storage) incur costs based on usage. You can use the portal to monitor and control these expenses.
How do I secure my Azure Portal environment?
Secure your Azure Portal by enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), using role-based access control (RBAC), applying least-privilege principles, and regularly reviewing user permissions. Integrate with Microsoft Defender for Cloud for advanced threat protection.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Yes, you can automate tasks using ARM templates, Azure CLI, PowerShell, or through integrations with Azure DevOps and GitHub. The portal also supports automated alerts, backups, and scaling rules.
Where can I learn more about Azure Portal features?
Visit the official Microsoft Learn documentation on the Azure Portal for tutorials, best practices, and updates on new features.
The Azure Portal is much more than a simple dashboard — it’s a comprehensive control center for your entire Azure journey. From deploying resources and securing identities to monitoring performance and managing costs, its features empower organizations to harness the full potential of the cloud. By mastering its tools and following best practices, you can streamline operations, reduce risks, and drive innovation across your IT landscape. Whether you’re just starting out or optimizing an existing setup, the Azure Portal remains an essential asset in today’s digital world.
Further Reading: