Azure Standard: 7 Powerful Insights You Must Know in 2024
Welcome to the ultimate guide on Azure Standard—your gateway to understanding Microsoft’s foundational cloud service tier. Whether you’re new to cloud computing or optimizing enterprise workloads, this deep dive reveals everything you need to know about performance, pricing, scalability, and real-world applications of Azure Standard.
What Is Azure Standard and Why It Matters

Azure Standard refers to Microsoft Azure’s core tier of virtual machines (VMs), storage, and services designed for production workloads that require reliable performance, high availability, and enterprise-grade support. Unlike the Basic tier, which is optimized for dev/test environments, Azure Standard is built for applications that demand consistent uptime, scalability, and integration with advanced Azure features like load balancing, auto-scaling, and managed disks.
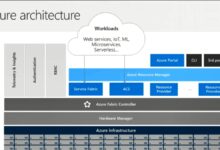
Defining Azure Standard in Cloud Architecture
Azure Standard sits at the heart of Microsoft’s Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offerings. It encompasses a wide range of VM sizes, storage options, and networking capabilities tailored for business-critical applications. These resources are hosted in globally distributed data centers, ensuring low latency and high redundancy.
- Supports both Windows and Linux operating systems
- Offers integration with Azure Active Directory, Backup, and Site Recovery
- Enables deployment through Azure Portal, CLI, PowerShell, or ARM templates
This tier is ideal for web servers, enterprise databases, application servers, and backend processing systems that cannot afford downtime.
Differentiating Azure Standard from Other Tiers
Microsoft Azure offers multiple service tiers, including Basic, Standard, and Premium. While Basic is cost-effective for non-critical workloads, Azure Standard provides enhanced capabilities:
Availability Sets: Ensures VMs are distributed across fault and update domains to minimize downtime during maintenance or hardware failures.Managed Disks: Azure Standard VMs can use managed disks, which simplify storage management and improve reliability.Load Balancer Integration: Standard-tier VMs can be integrated with Azure Load Balancer and Application Gateway for traffic distribution..
“Azure Standard is the go-to choice for organizations transitioning from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud with minimal disruption.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Azure Standard Virtual Machines: Types and Use Cases
One of the most widely used components under the Azure Standard umbrella is the Virtual Machine (VM).Azure offers a vast array of VM sizes categorized by compute, memory, and storage performance.Understanding these types helps businesses align their workloads with the right resources..
General Purpose VMs (A and D Series)
The A and D series VMs are classified as general-purpose and are part of the Azure Standard tier. They offer a balanced mix of CPU, memory, and disk resources, making them suitable for a wide variety of applications.
- D-series: These VMs are powered by Intel or AMD processors and provide solid-state drive (SSD) temporary storage, delivering better performance than the older A-series.
- A-series: Entry-level VMs ideal for development and testing, though still under the Standard tier when deployed with availability sets or load balancers.
Common use cases include small to medium web servers, domain controllers, and jump boxes.
Compute-Optimized VMs (F Series)
For workloads that require high CPU performance, such as batch processing, media encoding, or scientific simulations, the F-series VMs under Azure Standard are ideal.
- High CPU-to-memory ratio
- Supports up to 8 vCPUs and 16 GB RAM (F8s v2)
- Cost-effective for CPU-intensive applications
These VMs are often used in engineering simulations, financial modeling, and real-time data processing pipelines.
Memory-Optimized VMs (E and M Series)
When your application demands large amounts of RAM—such as in-memory databases, large caches, or enterprise ERP systems—the E and M series VMs are the preferred choice within Azure Standard.
- E-series: Enhanced memory VMs with up to 416 GB RAM (E80ids v4)
- M-series: High-memory VMs designed for SAP HANA and other in-memory workloads
- Supports premium SSDs for fast disk I/O
Organizations running SQL Server, Oracle, or SAP environments frequently deploy these VMs to ensure optimal performance.
Storage Options Under Azure Standard
Storage is a critical component of any cloud deployment, and Azure Standard provides several storage solutions tailored to different performance and cost requirements. From standard HDDs to SSD-backed disks, Azure ensures flexibility and reliability.
Standard HDD and SSD Managed Disks
Azure Standard includes two primary types of managed disks: Standard HDD and Standard SSD. These are cost-effective storage options suitable for development, testing, and non-latency-sensitive production workloads.
- Standard HDD: Best for infrequent access, backup storage, or low-priority applications
- Standard SSD: Offers better IOPS and lower latency than HDD, ideal for web servers and small databases
- Pricing is based on provisioned storage size, not actual usage
Both disk types are replicated within the data center for durability and can be attached to Azure Standard VMs seamlessly.
Integration with Azure Blob Storage
Beyond VM disks, Azure Standard environments often leverage Azure Blob Storage for unstructured data like images, videos, logs, and backups. While Blob Storage has its own pricing tiers (Hot, Cool, Archive), it integrates tightly with Standard-tier VMs.
- Mount Blob Storage via Azure Files or Storage Explorer
- Use AzCopy or REST APIs to transfer data efficiently
- Leverage lifecycle management to move data between tiers automatically
This integration allows businesses to scale storage independently of compute, reducing costs and improving manageability.
Disk Performance and Scalability
Understanding disk performance metrics—such as IOPS, throughput, and latency—is crucial when designing systems on Azure Standard. Each VM size has limits on the number of disks it can attach and the maximum IOPS it supports.
- Standard SSDs offer up to 6,000 IOPS per disk
- HDDs provide up to 500 IOPS per disk
- Throughput can reach up to 60 MB/s for SSDs
To maximize performance, administrators often use disk striping or caching strategies. Additionally, enabling read/write caching on OS and data disks can significantly boost application responsiveness.
Networking and Security in Azure Standard
Robust networking and security are non-negotiable for production systems. Azure Standard provides built-in tools to secure communication, manage traffic flow, and protect against threats—all without requiring third-party solutions.
Virtual Networks and Subnets
Azure Standard deployments typically reside within Virtual Networks (VNet), which act as private networks in the cloud. VNets allow segmentation of resources using subnets, enhancing security and traffic control.
- Define custom IP address ranges using CIDR notation
- Isolate tiers (e.g., web, app, database) into separate subnets
- Enable Network Security Groups (NSGs) to filter inbound and outbound traffic
VNets also support site-to-site and point-to-site VPNs, enabling hybrid cloud connectivity with on-premises infrastructure.
Load Balancing and Traffic Management
Azure Standard integrates with Azure Load Balancer and Application Gateway to distribute traffic across multiple VMs, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance.
- Azure Load Balancer: Operates at Layer 4 (TCP/UDP) and supports both public and internal load balancing
- Application Gateway: A Layer 7 load balancer that supports SSL termination, URL-based routing, and Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Both services are available in Standard SKUs with enhanced features like zone redundancy
For example, an e-commerce platform might use Application Gateway to route traffic to different backend pools based on URL paths (e.g., /cart, /checkout).
Security Best Practices for Azure Standard
Securing Azure Standard environments involves a multi-layered approach. Microsoft provides several native tools to enforce security policies and monitor threats.
- Enable Azure Security Center (now Microsoft Defender for Cloud) to detect vulnerabilities and recommend remediations
- Use Just-in-Time VM Access to limit open ports and reduce attack surface
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to enforce least-privilege principles
“Security is not a feature—it’s a continuous process. Azure Standard gives you the tools, but your team must apply them wisely.” — Microsoft Azure Security Guide
Pricing and Cost Optimization for Azure Standard
One of the biggest concerns for organizations adopting Azure Standard is cost management. While the tier offers robust performance, uncontrolled usage can lead to unexpected bills. Fortunately, Azure provides several mechanisms to optimize spending.
Understanding Azure Standard Pricing Model
Azure Standard follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you’re charged based on VM size, storage, and network usage. However, there are nuances to consider:
- VM costs are calculated per second (after the first minute)
- Managed disks are billed based on provisioned size, not actual data stored
- Data transfer out to the internet incurs additional fees
You can explore detailed pricing using the Azure Pricing Calculator, a powerful tool for estimating monthly costs.
Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
To reduce costs, organizations can purchase Reserved VM Instances (RIs) for one or three years. This commitment results in significant discounts—up to 72% compared to pay-as-you-go rates.
- RIs apply to specific VM sizes and regions
- Can be exchanged or refunded under certain conditions
- Savings Plans offer more flexibility by applying discounts across families or services
For predictable workloads (e.g., database servers), RIs are a smart financial move.
Auto-Shutdown and Right-Sizing Strategies
Many organizations waste money running VMs 24/7 when they’re only needed during business hours. Azure Standard supports auto-shutdown schedules to turn off VMs during off-peak times.
- Configure auto-shutdown via the Azure Portal or PowerShell
- Set notifications to alert administrators before shutdown
- Combine with monitoring tools to identify underutilized VMs
Additionally, right-sizing involves resizing VMs to match actual workload demands. For example, downgrading from a D8s v3 to a D4s v3 if CPU usage averages below 20%.
Monitoring and Management Tools for Azure Standard
Effective cloud operations require visibility into system performance, availability, and resource utilization. Azure Standard integrates with a suite of monitoring and management tools to help administrators maintain optimal performance.
Azure Monitor and Log Analytics
Azure Monitor is the central service for collecting, analyzing, and acting on telemetry data from Azure resources, including Standard-tier VMs.
- Collect metrics like CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network usage
- Create custom dashboards and alerts
- Integrate with Log Analytics for advanced querying using Kusto (KQL)
For example, you can set up an alert to notify your team if a VM’s CPU exceeds 90% for more than 5 minutes.
Automation with Azure Runbooks and Logic Apps
To reduce manual intervention, Azure Standard environments can be automated using Azure Automation and Logic Apps.
- Create runbooks to start/stop VMs, patch systems, or backup data
- Use Logic Apps to orchestrate workflows across Azure and third-party services
- Schedule tasks to run during maintenance windows
This automation not only improves efficiency but also reduces human error.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Options
Data loss can be catastrophic. Azure Standard supports robust backup and disaster recovery solutions through Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery.
- Azure Backup: Backs up VMs to a Recovery Services vault with retention policies up to 99 years
- Azure Site Recovery: Replicates VMs to a secondary region for failover during outages
- Both services integrate seamlessly with Standard-tier VMs
These tools ensure business continuity and compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Real-World Applications of Azure Standard
Theoretical knowledge is valuable, but real-world examples demonstrate how Azure Standard delivers tangible benefits. Let’s explore how different industries leverage this tier for mission-critical operations.
Healthcare: Secure Patient Data Management
A healthcare provider in the U.S. migrated its electronic health record (EHR) system to Azure Standard VMs running Windows Server and SQL Server. By using E-series VMs with Standard SSDs, they achieved sub-second query response times while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
- Used NSGs and Azure Firewall to protect patient data
- Enabled Azure Backup for daily snapshots
- Leveraged Azure Monitor for 24/7 system health tracking
The result was a 40% reduction in infrastructure costs and improved system reliability.
Retail: Scalable E-Commerce Platforms
A global retail brand used Azure Standard to host its e-commerce platform during peak shopping seasons. They deployed D-series VMs behind an Application Gateway with auto-scaling rules.
- Auto-scaled from 10 to 50 VMs during Black Friday
- Used Standard SSDs for fast product catalog loading
- Leveraged CDN and Blob Storage for image delivery
This architecture handled over 1 million concurrent users without downtime.
Manufacturing: IoT and Predictive Maintenance
An industrial manufacturer deployed Azure Standard VMs to process data from thousands of IoT sensors on factory equipment. F-series VMs processed real-time telemetry, while E-series VMs ran machine learning models for predictive maintenance.
- Data ingested via Azure IoT Hub and stored in Blob Storage
- Used Azure Databricks on Standard VMs for analytics
- Triggered alerts when equipment anomalies were detected
This implementation reduced unplanned downtime by 35%.
Future Trends and Evolution of Azure Standard
As cloud technology evolves, so does Azure Standard. Microsoft continuously enhances this tier with new features, performance improvements, and integration with emerging technologies.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Azure Standard VMs are increasingly being used as entry points for AI and ML workloads. While GPU-intensive tasks require NV-series VMs, many preprocessing and inference tasks run efficiently on Standard-tier instances.
- Data cleaning and transformation on D-series VMs
- Model deployment using Azure Machine Learning on E-series VMs
- Integration with Azure Cognitive Services for vision, speech, and language APIs
This democratizes AI access for organizations that can’t afford premium GPU instances.
Edge Computing and Hybrid Scenarios
With the rise of edge computing, Azure Standard plays a role in hybrid architectures. Azure Stack, which brings Azure services on-premises, uses Standard-tier principles for consistency.
- Run the same VM images on-prem and in the cloud
- Use Azure Arc to manage Standard VMs across environments
- Enable low-latency processing for IoT and real-time analytics
This convergence simplifies operations and reduces vendor lock-in.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Initiatives
Microsoft is committed to sustainability, aiming for carbon-negative operations by 2030. Azure Standard contributes by optimizing resource utilization and promoting energy-efficient computing.
- Right-sizing reduces unnecessary energy consumption
- Auto-shutdown policies lower power usage
- Azure’s global data centers use renewable energy sources
Organizations using Azure Standard can report lower carbon footprints as part of their ESG goals.
What is Azure Standard used for?
Azure Standard is used for hosting production workloads such as web servers, enterprise databases, application servers, and backend systems that require high availability, scalability, and integration with Azure’s advanced networking and security features.
How does Azure Standard differ from Basic and Premium tiers?
Azure Standard offers better availability, support for managed disks, and integration with load balancers compared to the Basic tier. Unlike Premium, which focuses on high-performance SSDs and ultra-low latency, Standard balances cost and performance for general production use.
Can I save money on Azure Standard?
Yes, you can save money by using Reserved Instances, Savings Plans, auto-shutdown policies, and right-sizing VMs. Monitoring tools like Azure Cost Management help identify cost-saving opportunities.
Is Azure Standard suitable for AI workloads?
While not optimized for GPU-heavy AI training, Azure Standard is suitable for data preprocessing, model inference, and deploying machine learning models via Azure Machine Learning.
How do I secure my Azure Standard environment?
Use Network Security Groups, Azure Firewall, Just-in-Time access, RBAC, and Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Regularly apply updates and follow the Azure Security Benchmark.
In conclusion, Azure Standard is more than just a cloud service tier—it’s a strategic foundation for modern IT infrastructure. From virtual machines and storage to networking, security, and cost management, it offers a comprehensive suite of tools for businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re migrating legacy systems, scaling e-commerce platforms, or building data-driven applications, Azure Standard provides the reliability, flexibility, and performance you need. As cloud technology advances, this tier will continue to evolve, integrating with AI, edge computing, and sustainability initiatives to meet future demands. By understanding its capabilities and best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of Microsoft Azure while maintaining control over costs and security.
Further Reading: